Continuing from my previous post, here is how to create an attack heat map in seconds using the same ElasticSearch + Kibana instance. First of all we have to download Maxmind’s GeoIP database. The general procedure is super easy (no need to do it):
wget -N http://geolite.maxmind.com/download/geoip/database/GeoLiteCountry/GeoIP.dat.gz gunzip GeoIP.dat.gz
This will output a single GeoIP.dat file which is a binary format with IP to geolocation data mappings which you can query using an API. The Python version of the latter is easily installable via pip (do this):
pip install GeoIP
Bear in mind that you’ll probably get the “clang: error: unknown argument” failure message but fear not; I have written the solution here if you need it: /bypassing-clang-error-unknown-argument.html
We then have to modify the script I posted a little bit, in order to save the two letter country code in the JSON documents before indexing them in ElasticSearch. I have actually decided to pursue this project and publish the (poorly written at this stage, serving as an example) code properly. So just get the Kippo2ElasticSearch files from GitHub:
git clone https://github.com/ikoniaris/kippo2elasticsearch
It includes the GeoIP database, no need to get it yourself. Edit the MySQL and ES values and you’re ready. After importing the data to ElasticSearch, open Kibana and add a new map panel:
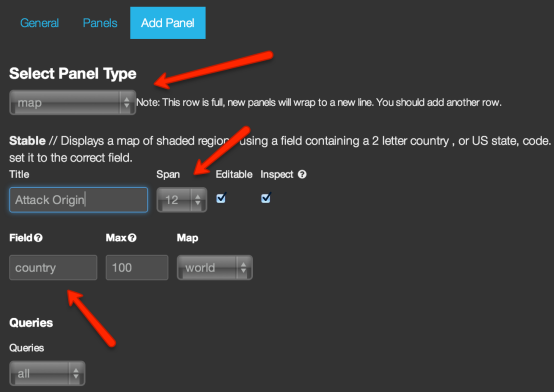 And voilà, scroll down and you’ll have a heatmap of attacks:
And voilà, scroll down and you’ll have a heatmap of attacks:
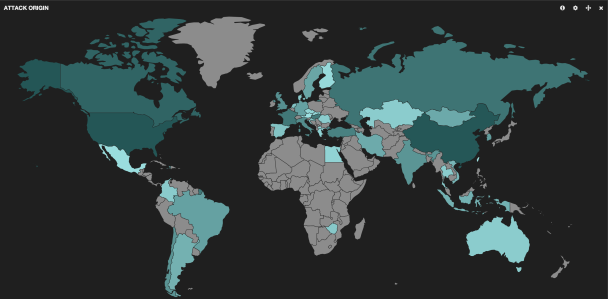 Do you really need more convincing about the prospects of a project combing honeypots with ElasticSearch + Kibana?
Do you really need more convincing about the prospects of a project combing honeypots with ElasticSearch + Kibana? 
For comments, suggestions, fixes, please use the Kippo2ElasticSearch page: /kippo2elasticsearch

Pingback: Security-Vision » Kippo attack heatmap in seconds using Kibana and Kippo2ElasticSearch()
Pingback: Adding ElasticSearch support to Kippo SSH honeypot - BruteForce Lab's Blog()